The SaaS (software-as-a-service) business model is an essential tool for scaling and measuring your company’s growth. Numbers are crucial for development, and keeping track of them is even more critical.
Identifying the right metrics at the right time can provide businesses with various action plans. It couldn’t be said better than by Lord Kevin:
If you can’t measure it, you can’t improve it.
SaaS business models are more complex than conventional business models. SaaS captures metrics that traditional business models fail to measure. Without measuring key performance indicators (KPI), companies can ignore alarming signs of potential customer and revenue losses.
So how do we measure KPIs and the success of SaaS business models?
Important Metrics to Measure the Success of Your SaaS Business Model
 There are a vast number of metrics that can monitor your business, but not all metrics are suited for your business. Different metrics can help analyze other parts of your company’s sales funnel.
There are a vast number of metrics that can monitor your business, but not all metrics are suited for your business. Different metrics can help analyze other parts of your company’s sales funnel.
The first task is to identify the right metrics to measure for your company. To specify those, perform the following:
- Identify your company’s goals.
- Identify those metrics that can help you achieve those goals.
- Prioritize metrics that have an impact on your business.
- Create a plan of action to improve underlying metrics.
When you have identified the underlying metrics affecting your company, start working on improving these with your team.
Churn Rates
Churn rates are an essential metric to measure for businesses. There are two types of churn rates.
Customer Churn
Customer churn rates measure how many customers a company has lost in a specific time period; it is typically measured annually or monthly. If there is a consistent increase in churn rates, potential causes of customer losses need to be identified and a plan to retain customers should be created. We can calculate churn rates like this:
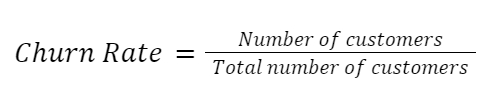
Revenue Churn Rate
The Revenue Churn Rate (RCR) is similar to the customer churn rate; instead of customers, revenue loss is calculated for a given time period. Calculate RCR by:
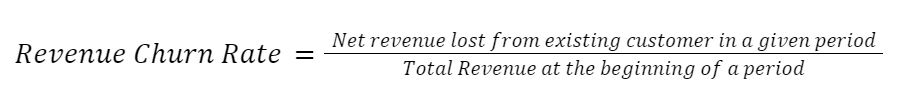
Churn rates provide a detailed analysis of how a business retains its customers. It highlights the areas where improvement is needed. Maybe your product is not performing up to the customer’s expectations or you have bad customer service. Whatever the reason, maybe there is always room for improvement.
Churn rates have a significant impact on large enterprises as a slight change in rates can result in a massive loss of customers and revenue. Negative churn rates for small and medium enterprises are also a warning sign, but they usually have a small pool of customers they can cover with minimum effort.
Monthly Recurring Revenue
Monthly recurring revenue (MRR), a useful metric, is the amount generated from your customers. Knowing your monthly revenue can help to create new goals and road maps for new and existing plans. MRR helps to forecast future financial growth.
The following equation details how to determine MMR:
MRR=Number of customers x average monthly billing amount
MRR Growth Rate
MRR growth rate details whether MRR has improved or decreased over time. It is an essential metric that can help the company to track performance and momentum and determine performance.
A company with an increase in MRR growth rate is showing increasing revenues. MRR growth rate is calculated as follows:
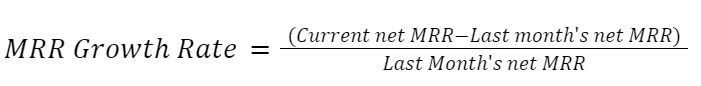
As an example of MRR growth rate, if your company had a $100,000 net MRR for March and your net MRR for April was $110,000, your company had a 10% MRR growth rate; this is a positive sign; try to increase it or maintain this rate.
Annual Recurring Revenue
 Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR) is the total revenue a company collects from its customers in a 12-month period. ARR is measured annually, unlike MRR, which is calculated every month.
Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR) is the total revenue a company collects from its customers in a 12-month period. ARR is measured annually, unlike MRR, which is calculated every month.
ARR has a simple method of calculation:
ARR=MRR x 12
ARR is another useful metric to measure the success of your SaaS business model. Through MRR and ARR, you can determine how much value you are providing customers by keeping track of revenues monthly and annually.
Monitoring metrics, forecasting cash flows, analyzing trends, and developing new goals are vital factors for a business’s sustainability.
Customer Acquisition Cost
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) is the amount a company spends to acquire a new customer. CAC consists of all amounts spent on a customer, including marketing expenses, sales expenses, staff salaries, digital media ads spending, print media advertising amounts, and other technical costs.
Businesses should not exceed CAC more than the profit generated through acquired customers. Otherwise, the company won’t be profitable. CAC is calculated as:

CAC can be minimized by utilizing various marketing channels to determine which ones produce the highest return with the minimal amount budgeted. Reducing CAC can increase growth rates while limiting budgetary expenses.
Customer Lifetime Value
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV or LTV) is the total revenue generated during a customer’s lifespan of subscribing to your services or products. To calculate CLV, consider three items:
- CAC
- Annual revenues per customer
- A customer’s lifespan
Thus, CAC is calculated by:
CLV=Annual revenue per customer x customer’s lifetime=CAC
CLV determines how profitable a customer can be in the long run while allowing a business to adjust campaigns and strategies accordingly.
CLV should be greater than CAC. Ideally, CLV should be three times more than the amount spent on CAC.
LTV>(3 x CAC)
Conversion Rate
Conversion Rate (CR) determines whether a company is heading in the right direction or not. CR is an essential tool to measure the success of your SaaS businesses model. CR calculates the percentage of potential customers who turn into paying customers for a business.
Not all visitors to your business are potential buyers. CR determines how a marketing campaign targets the right audience for your company.
For example, you run an ad campaign on social media for your services. The ad targets a large audience, and many of them see your ad, which is called an “impression.” At the same time, some customers view your ad and then buy your services or products. These numbers are called conversions.
CR is calculated by:
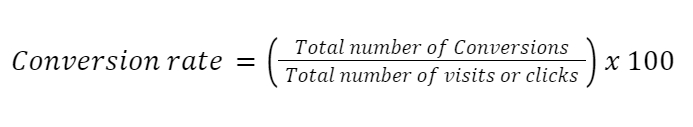
Net Promoter Score
Net Promoter Score (NPS) details the value customers gain from your products or services. Companies can use simple feedback forms to measure NPS.
NPS determines whether your customers are satisfied with your products or services; if they are, they are likely to repurchase again. However, if customers have a terrible experience, this increases the customer and revenue churn ratio.
NPS is extremely useful to determine the success or failure of currently launched projects and future planned projects or when establishing a new product or service.
Marketing Qualified Leads
 Marketing Qualified Leads (MQLs) are potential customers who have shown some curiosity or interest in your brand through any marketing channels you use. For example, someone subscribed to your newsletter, downloaded an e-book, contacted you on your online chat, or created an account on your website.
Marketing Qualified Leads (MQLs) are potential customers who have shown some curiosity or interest in your brand through any marketing channels you use. For example, someone subscribed to your newsletter, downloaded an e-book, contacted you on your online chat, or created an account on your website.
Not all MQLs are valuable as some have different commitment levels to your business. To illustrate, people who just signed up for your newsletter or visited your website are less valuable than leads who created an account on your website and logged in there.
Customer Retention Cost
Customer Retention Cost (CRC) is the investment required to retain a customer. Like other metrics, this one is also beneficial for measuring how much financial investment a company expends into maintaining a customer.
Poor strategies can result in losses in CRC but more revenue can result by retaining clients. CRC per customer can be calculated by:
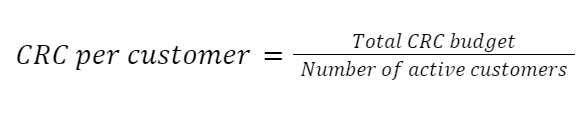
Customer Retention Rate
Customer Retention Rate (CRR) calculates how many customers your company retained over a given period, which can be a month, year, or even a quarter. A good CRR relates to excellent customer service. CRR is determined by:

CRR determines a company’s efficiency at customer satisfaction and how effective customer service is in addressing customers’ queries and issues.
Let Orases Handle All Your SaaS Projects
To learn more about the most effective key performance indicators for your business, reach out to the professionals at Orases. Our KPI experts can schedule a consultation to develop strategies and plans for improving your metrics.






