Software as a Service (SaaS) companies are organizations that host an application and make it available to customers over the internet. According to a report by Gartner, SaaS is one of the largest and fastest-growing market segments with a growth forecast of more than $104.7 billion.
One of the biggest decisions that SaaS businesses have to make involves choosing a pricing model. Companies often spend significant time, money and energy creating an amazing product only to undervalue their worth. Choosing the right pricing model can help these businesses approach different SaaS pricing strategies in a way that supports the organization’s growth and success.
What Are SaaS Pricing Models?
A SaaS pricing model refers to how a business packages the pricing of a product or service. SaaS pricing models help organizations determine how to identify a realistic price that people are willing to pay but will still generate a profit.
There are several factors to consider when choosing an SaaS pricing model, such as where the business will position itself in the market, who the target audience is, how many customers are likely to be served and the main benefits that these customers will receive.
Organizations should also consider how to form their ideal SaaS team and who they serve, such as direct customers (B2C), businesses (B2B) or both. With this information in mind, businesses can better understand the value of their SaaS and strategically consider pricing bundles and tiers.
Types Of SaaS Pricing Models
Software as a Service differs from traditional sales models. SaaS is a subscription-based service for which customers pay their provider on a regular basis for the continued use of a product or service. The strategies used to set subscription prices are different from the strategies used to set prices on regular products and services. SaaS is often presented in complex packages which requires businesses to place more consideration into their pricing.
There are many different types of SaaS pricing models to consider, such as the following:
1. Flat-Rate Pricing Model
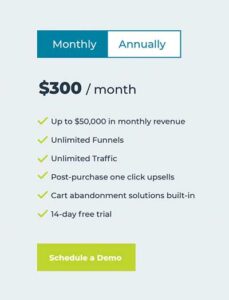
Figure 1.1 — Flat Rate Pricing Model Example
A flat-rate SaaS pricing model offers a product, with specified features, at a predetermined price point. Customers do not get to choose from different pricing options or features. Instead, the flat-rate pricing model takes on a “one size fits all” approach by which customers are charged the same amount on a monthly or annual basis despite how many users are using the product or service.
There are many advantages to using flat-rate pricing models; they are easy to use and understand, making them a great choice for a wide range of businesses. A flat-rate pricing model also makes forecasting revenue more accurate since there are no varying costs or complications that must be factored into the price.
There are also some disadvantages to using SaaS pricing models. The one size fits all approach is not suitable for all businesses; with some businesses, customers prefer to have a choice in the cost and features of the product they purchase. Flat-rate SaaS pricing models also do not allow the buyer to upgrade plans, which eliminates the opportunity to upsell.
2. Tiered Pricing Model
Tiered pricing models are another common type of pricing model based on the tiered SaaS pricing strategy. Under a tiered pricing model, multiple versions of a product are offered to customers at different prices. The cost of these products is generally based on factors such as features, usage or the number of users.
Typically, two to five tiers are created allowing the customer to choose which tier best suits their needs based on the specific features offered in that particular tier. Tiered pricing models enable businesses to upsell to their customers and scale up available features. It is important that the tiers created for a product are carefully constructed to make it clear what is being offered and minimize confusion.

Figure 1.2 — Tiered Pricing Model Example
There are several key advantages to tiered SaaS pricing models. This type of model appeals to a variety of customers, giving them the option to choose what plan best works for them. However, it is important to understand that as each tier increases, the customer’s decision-making process becomes more complex.
3. Usage-Based Model
Commonly known as the ‘pay as you go’ model, the usage-based SaaS pricing model occurs when a customer is charged for a product or service based on their usage. The more the customer uses a product or service, the more they are charged. Conversely, if they use it less, they are charged less during that pay period. Usage may include a variety of activities, such as sending emails, making phone calls or completing transactions.

Figure 1.3 — Usage-Based Pricing Model Example
Many customers favor usage-based pricing models which allows them to pay only the amount that is proportional to their usage. This pricing design can also be easily adapted to fluctuations in a customer’s business. There are also some downsides to usage-based pricing models to consider. Predicting revenue can often be challenging since it is based on the variable of the customer’s usage of the product or service.
4. Per-User Model
Per-user SaaS pricing models allow businesses to charge customers based on the number of users that use the product. Under this type of SaaS pricing model, every account is charged which makes it easier to predict future revenue.
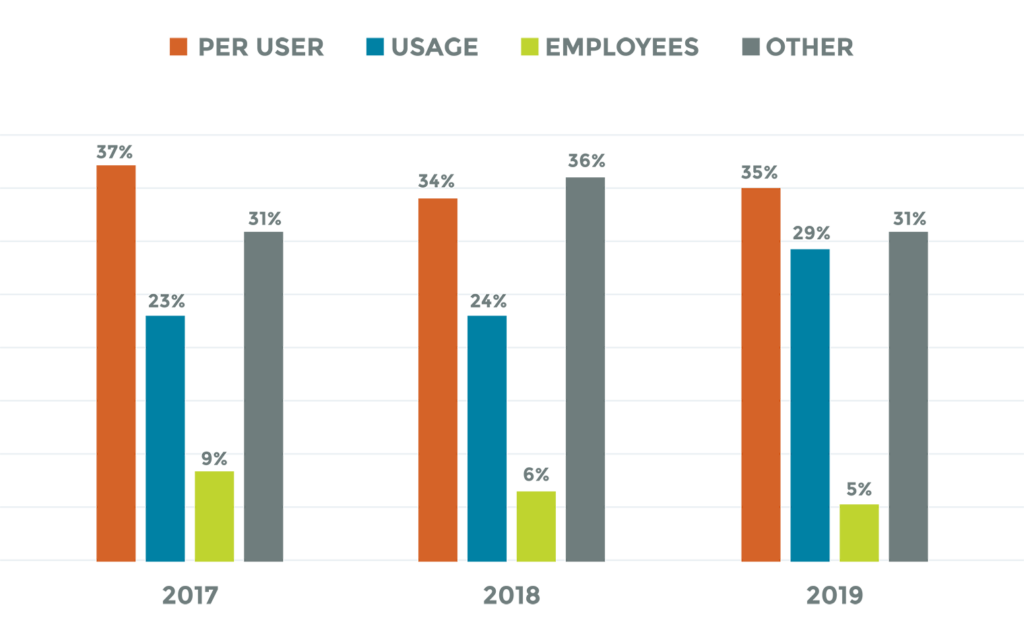
Figure 1.4 — Per-User Pricing Model Example
Businesses can enjoy many benefits when they switch to a per-user pricing model. This model is generally easier to understand for customers as the amount charged is based strictly on the number of people using the product. Each user is given access to the product and there is no upselling. However, some businesses implement a limit as to how many users can use the product as a cost-cutting measure.
5. Per-Feature Model
Customers are charged based on features and functionalities chosen when using a per-feature SaaS pricing model. The more features that a customer chooses, the higher the cost of the product or service. Per-feature pricing models often consist of tiers that each have their own price and set of features. These tiers enable the SaaS provider to engage in upselling.

Figure 1.5 — Per-Feature Pricing Model Example
Many customers enjoy per-feature pricing models as they only have to pay for the features and functions that they actually want. This can also save money as customers do not need to pay for unnecessary features. As it is not always easy to determine what features customers are looking for, a per-feature pricing model can be challenging to create. A customer may also be against add-on features and may choose to avoid upgraded versions of the product.
6. Freemium Model
Freemium is a common SaaS pricing model in which businesses entice customers to sign up for a free, limited version of the product. This ‘trial’ version allows users to use the product for a certain amount of time before they will need to purchase it to continue using the paid version.

Figure 1.6 — Freemium Pricing Model Example
Freemium pricing models open up many opportunities for additional sales. Ads can be strategically placed on the product to encourage users to click. Unfortunately, only a small number of users will ultimately convert to paying customers.
7. Per Active User Model
Using a per active user SaaS pricing model, subscribers are charged based on how active they are while using the product or service. Although a team is able to enroll as many users as they would like, the customer is only charged when the product is actually used.
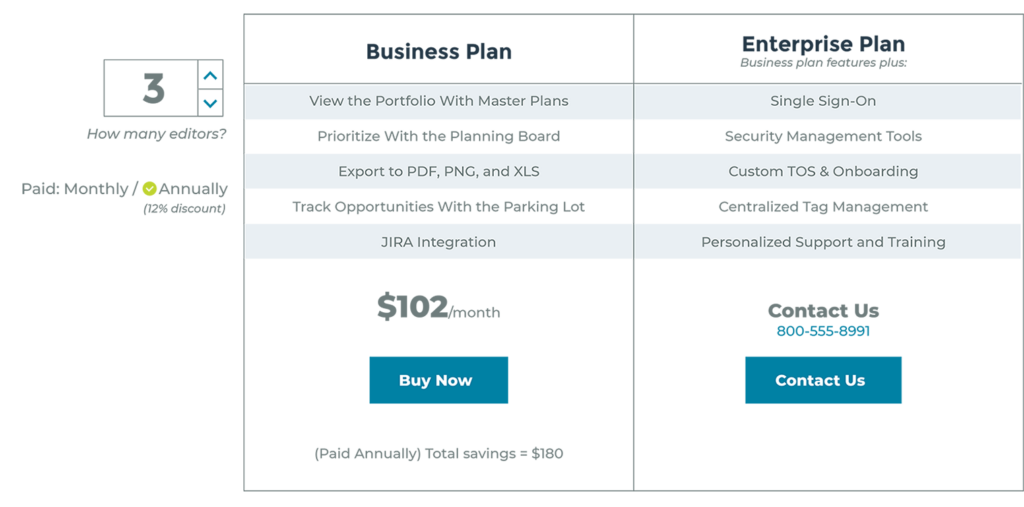
Figure 1.7 — Per Active User Pricing Model Example
There are many advantages to per active user pricing models. Money is not wasted on inactive users since only active users pay for the product. However, this type of SaaS pricing model is not well suited for smaller businesses where all members of the team use the application on a regular basis.
The Business Owner’s Handbook For SaaS Applications
Custom SaaS applications and the SaaS model can be very advantageous for businesses, especially when implementing the right type of SaaS pricing model. We’ve created a handbook for business owners interested in developing a custom SaaS application, organizing a SaaS team and moving towards a SaaS business model.
View SaaS Handbook
Choosing The Right SaaS Pricing Model
With so many SaaS pricing models available, it can be difficult to choose the best one for the business. When comparing different options, it is important to not only think about what is best for the company but also what is best for the customer.
 Prices do not influence just one department within the business. The decision should be made based on input from leaders in all departments, including sales, marketing, product and management.
Prices do not influence just one department within the business. The decision should be made based on input from leaders in all departments, including sales, marketing, product and management.
Thorough research will help businesses in the process to select an SaaS pricing model. It is also helpful to create buyer personas from any data collected in order to determine who the target audience is, what products they are looking for and how they will likely use the product. Also consider different ways to price the product based on features, cost and usage.
Feedback from existing customers, as well as from potential customers, can also be helpful when choosing an SaaS pricing model. Try to learn as much as possible about what it is that customers want from the product or service, and how improvements can be made by implementing changes in the pricing model.
Reach Out To Experienced SaaS Application Developers
When it comes to SaaS pricing models, it is important to remember that product prices are not set in stone. They can be modified or updated at any point to meet the needs of the business and to align with growth. Ideally, pricing should continue to scale along with the product and reflect the true value of the product. SaaS pricing models can be useful for businesses that need guidance when setting prices for their products or services.
With the assistance of an experienced SaaS application development company, modern businesses can create highly successful SaaS applications that are priced accurately and leave plenty of room for profit generation. For more information about how to choose an SaaS pricing model or to speak with an SaaS application development team, contact Orases by calling 301.756.5527 or by requesting a consultation online.






