A Successful Data Strategy: The Ultimate Guide
Learn how structured data initiatives can improve decision-making, streamline operations, break down silos, and ensure long-term growth through automation, governance, and a single source of truth.
The Power of Trustworthy Data for Your Business
Data has become one of the most valuable assets for modern organizations, empowering operational efficiencies, fostering innovation, and enhancing strategic agility. However, without a well-defined data strategy, data can quickly become a source of cost and complexity rather than value.
A successful data strategy provides a structured approach to managing data, ensuring it’s trustworthy, accessible, and aligned with business goals. By strategically implementing data initiatives, companies can achieve measurable ROI, whether through streamlined processes, improved decision-making, or enhanced customer experiences.
This guide offers an effective approach to data strategy, covering every key component required to align data with organizational objectives. It’s designed to help executives take actionable steps that turn data into a core part of business success, from initial goal-setting to advanced automation and lifecycle management.
01
Chapter 01
Why The Data Makes The Difference
Incorporating a strong data strategy is not just about managing data effectively; it’s about building a foundation that supports operational efficiency, informed decision-making, and business agility. A well-defined data strategy can be a powerful enabler for competitive advantage, driving significant gains across various aspects of an organization.
Improved Decision-Making Through Real-Time Data Access
Organizations with a well-implemented data strategy gain quicker access to reliable, real-time data, empowering leaders to make data-driven decisions. McKinsey reports that data-driven companies are 23 times more likely to acquire new customers and 19 times more likely to achieve profitability.
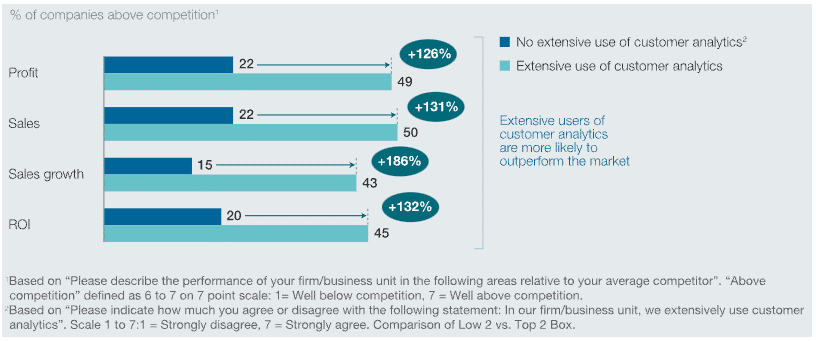
Faster, More Accurate Insights With Data Integration & Reduced Silos
Data silos, isolated pockets of data within departments or systems, are a common obstacle in organizations with legacy data structures. Silos create barriers to collaboration, limit visibility, and delay access to critical information, often leading to redundant work and inconsistent data across teams.
An integrated data strategy consolidates data across systems and departments, providing a “single pane of glass” view of the entire organization. This approach improves productivity by eliminating redundant processes and ensuring that all teams access the same accurate, up-to-date data.

Data analytics & visualization software provides insight into current market trends & patterns, and converts the data into visualizations.
Enhanced Data Quality & Integrity
A structured data strategy ensures data consistency and accuracy by standardizing processes and centralizing data governance. According to Gartner, poor data quality costs businesses an average of $12.9 million annually. By implementing data governance policies and quality checks, organizations can reduce errors and inefficiencies.
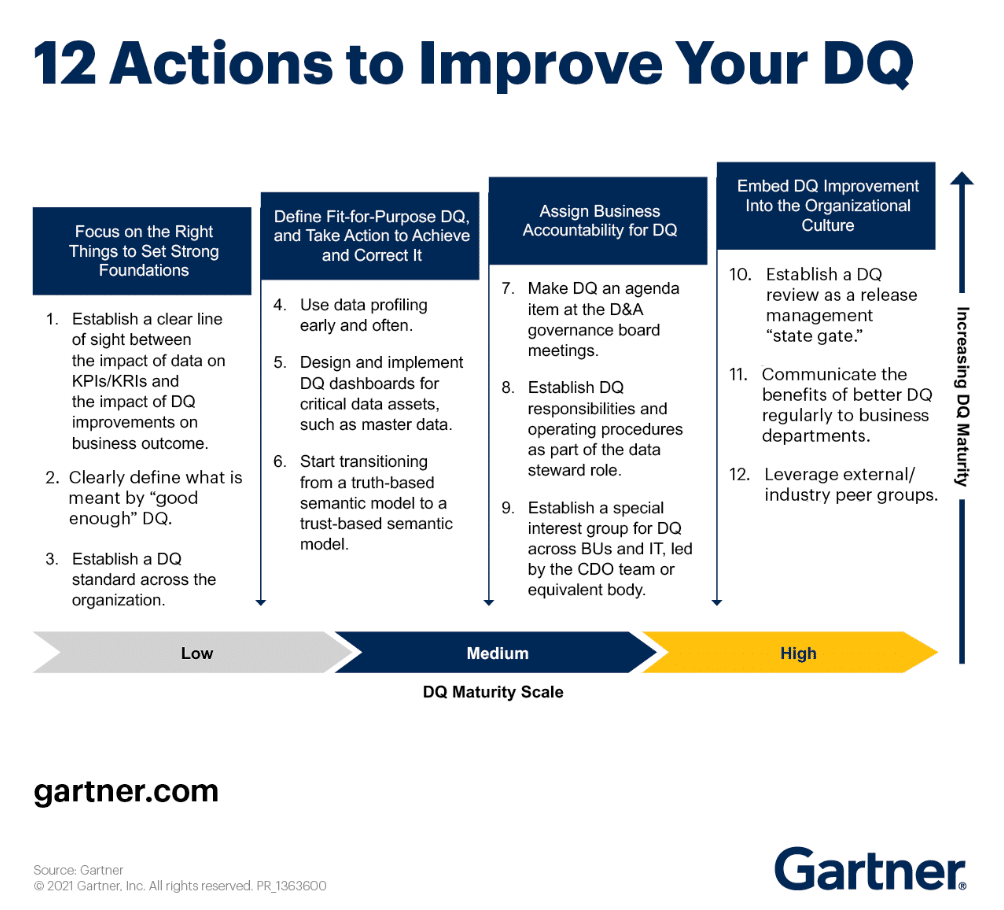
Scalability & Agility For Future Growth
A flexible, scalable data strategy prepares an organization for future growth and digital transformation. Cloud-based and modular data architectures support seamless scaling to meet evolving business needs.
According to a 2023 HashiCorp survey, 90% of respondents reported using multi-cloud infrastructure, highlighting the importance of scalable data strategies in modern enterprises.
02
Chapter 02
Setting Clear, Measurable Goals for Data-Driven Success
A successful data strategy is grounded in clearly defined goals aligned with specific business outcomes. Effective data goals are actionable and measurable, aiming to enhance operational efficiency, customer experience, or market positioning.
Aligning with Business Objectives
Start by identifying key business goals that could benefit from a data-driven approach. Aligning data initiatives with these goals ensures that investments translate to measurable ROI.
Key Questions for Defining Goals
- What business outcomes (e.g., revenue growth, cost savings) are we aiming to achieve?
- How will we measure success, and what KPIs will we track?
- What specific challenges—like data silos—currently limit these goals?
03
Chapter 03
Conducting a Data Landscape Assessment
A comprehensive assessment of the existing data environment provides a baseline for strategic planning. This process involves identifying data sources, access points, and departmental silos.
Mapping Data Sources and Silos
Organizations often discover data stored in isolated systems or “data silos,” where it’s inaccessible to other teams. Mapping these sources reveals opportunities for improved integration and utility.
Identifying Pain Points
Assess pain points like inconsistent naming conventions, inaccessible data, or bottlenecks that prevent data flow. Identifying these issues allows for targeted improvement steps.
Harvard Business Review highlights that organizations with streamlined data structures reduce data handling costs by up to 30%.
04
Chapter 04
Building a Culture of Continuous Review and Improvement
A data strategy must be a living framework that evolves with changing business needs. Regular reviews and audits ensure that data management practices remain effective and relevant.
Continuous Data Quality Audits
Regular audits of data quality reveal trends and ensure that data remains reliable over time, supporting accurate, insightful decision-making.
System and Process Evaluation
Evaluate KPIs related to system performance, user adoption, and pain points to refine data practices based on evolving needs.
McKinsey reports that companies updating data management practices based on new needs see a 40% increase in satisfaction among internal data users.
05
Chapter 05
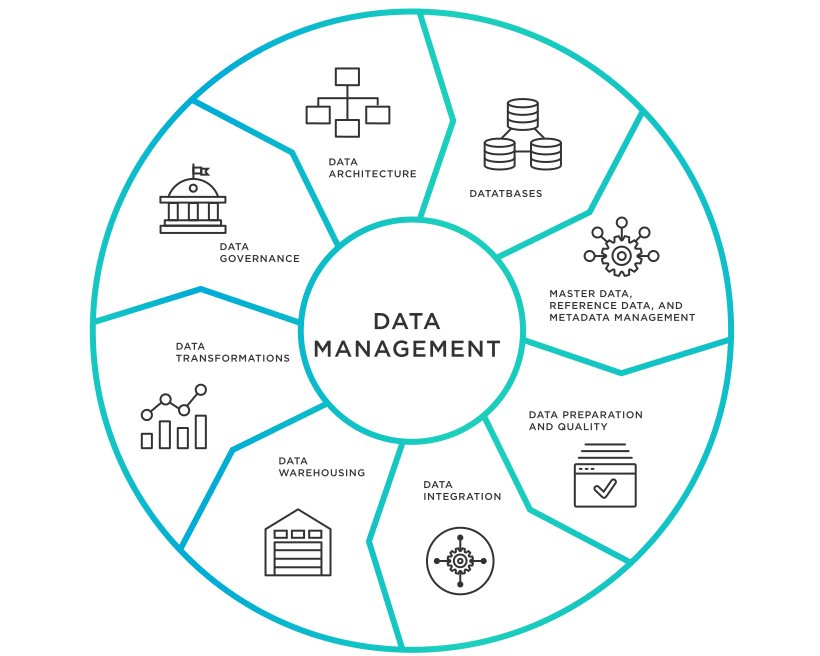
Effective Data Lifecycle Management and Governance
Data lifecycle management involves overseeing data from creation to disposal, ensuring it remains accessible, secure, and aligned with organizational standards. A Deloitte study found that organizations using data lifecycle standards increased data accessibility across teams by 25%.
An effective data lifecycle strategy not only protects data integrity but also optimizes its usability across departments.
Ownership and Access Control
Clearly defined ownership and permissions are essential to maintaining data integrity, especially for sensitive or regulated data. Role-based access control (RBAC) and attribute-based access control (ABAC) frameworks enable organizations to assign permissions based on job roles, data sensitivity, and access levels.
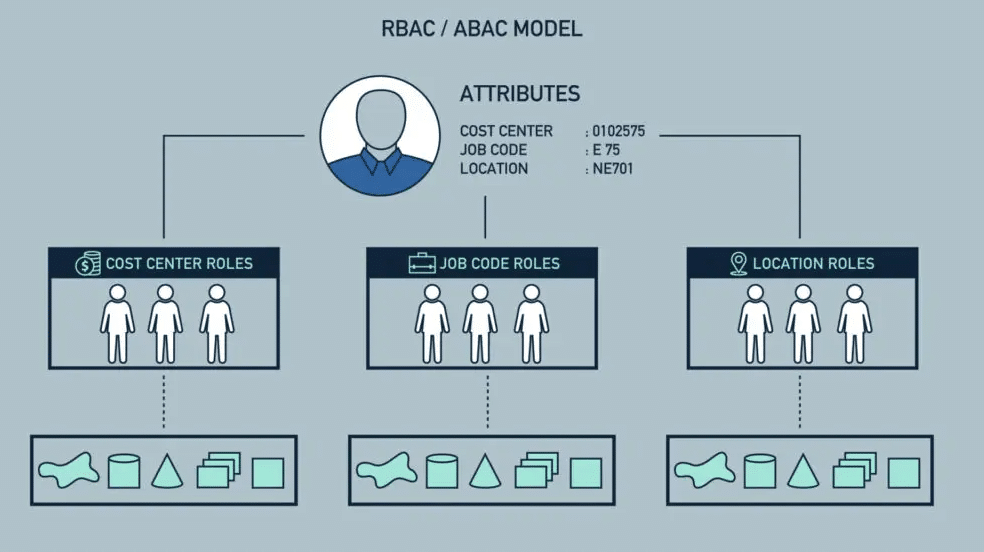
Access controls should align with data governance policies, ensuring compliance with standards like GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA. For instance, using tools like Active Directory or Okta for identity and access management (IAM) can streamline the enforcement of data access policies and prevent unauthorized access.
Data Standardization & Consistency
Standardizing terminology, formats, and naming conventions across the organization ensures consistent data usage and reduces the risk of errors. Implementing a master data management (MDM) system, such as Informatica MDM or SAP Master Data Governance, can help enforce consistency across teams and prevent discrepancies.
Standardization also extends to data formatting (e.g., date formats, currency symbols) and metadata tagging, which enhances data discoverability and usability, especially in organizations with complex data environments.
Automated Data Classification and Tagging
Automated classification tools, like Microsoft Azure Information Protection or IBM Watson Knowledge Catalog, can tag data based on its sensitivity level, department of origin, or intended use. This allows organizations to apply data handling policies automatically, improving security and compliance.
Data tagging facilitates data retrieval, enabling teams to search, filter, and access relevant data more efficiently. By categorizing data assets consistently, organizations can enhance data accessibility and reduce retrieval times across departments.
Data Retention & Disposal Policies
Establishing clear policies for data retention and disposal is crucial for regulatory compliance and optimizing storage costs. For example, data retention schedules based on data type and regulatory requirements (e.g., retaining financial records for seven years) ensure that data is available when needed and securely deleted when it is no longer useful.
Automated data lifecycle management tools, such as AWS Lifecycle Policies or Google Cloud Data Retention, can help enforce retention schedules by archiving or deleting data according to pre-set policies, reducing storage costs and minimizing the risk of data breaches.
06
Chapter 06
Breaking Down Data Silos & Improving Internal Communication
Encouraging collaboration and shared goals fosters a unified approach, reducing data silos and improving cross-departmental data use. Data silos not only hinder collaboration but also slow down decision-making, as teams lack a unified view of the organization’s data. This fragmentation results in delays in accessing accurate information, which in turn hampers responsiveness to market shifts and operational needs.
API-Driven Integration
APIs enable applications to communicate with each other, creating connections between disparate systems and eliminating silos without extensive re-architecting. By implementing API gateways and RESTful or GraphQL APIs, organizations can integrate legacy systems with modern data platforms, improving data flow and interoperability.
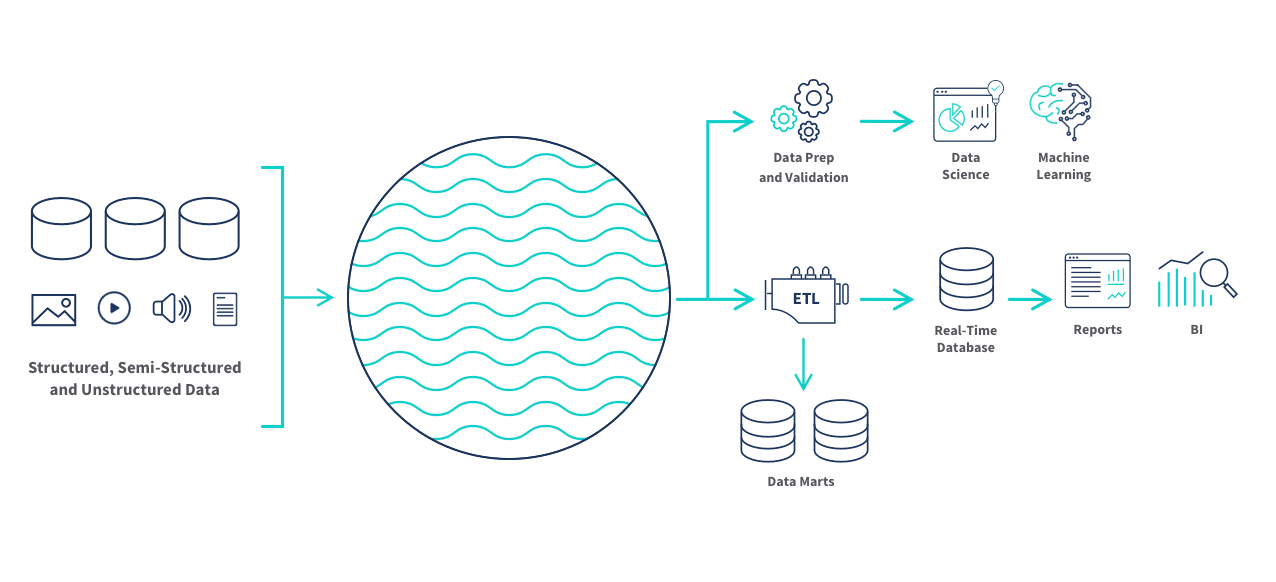
Data Warehousing and Data Lakes
Data warehouses and data lakes serve as centralized storage solutions, aggregating data from multiple sources in one location. Tools like Snowflake, Google BigQuery, and Amazon Redshift allow organizations to standardize and query data across departments, enabling holistic insights and reducing dependencies on siloed systems.
Master Data Management (MDM)
MDM establishes a single, authoritative view of key data entities (e.g., customers, products) across the organization, ensuring consistency and accuracy. By implementing MDM practices, organizations reduce discrepancies and duplicate records, which are common issues in siloed environments.

Ready to transform your data into actionable insights? Schedule a consultation today to develop a tailored data strategy that drives growth and efficiency for your business.
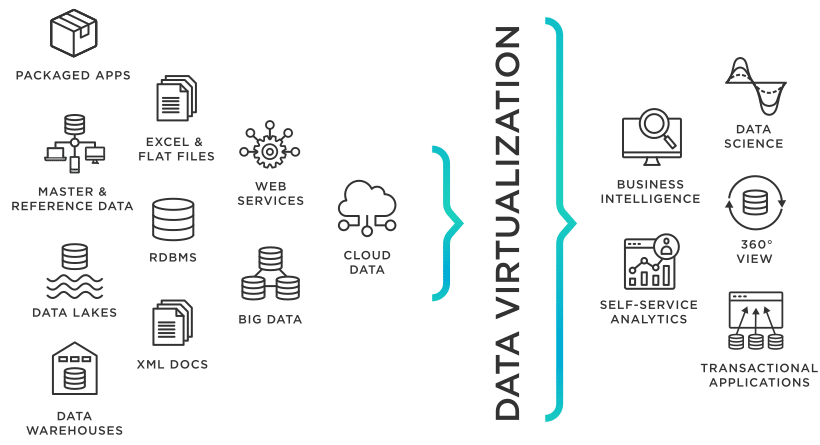
Data Virtualization
Data virtualization tools, such as Denodo and TIBCO, allow teams to access and analyze data across various systems without physically moving it. This approach provides a unified view of data from multiple sources, enabling faster insights while maintaining data integrity.
07
Chapter 07
Balancing Structure and Flexibility in Data Strategy
A successful data strategy balances structured processes with the flexibility for innovation and problem-solving.
Agile Data Management
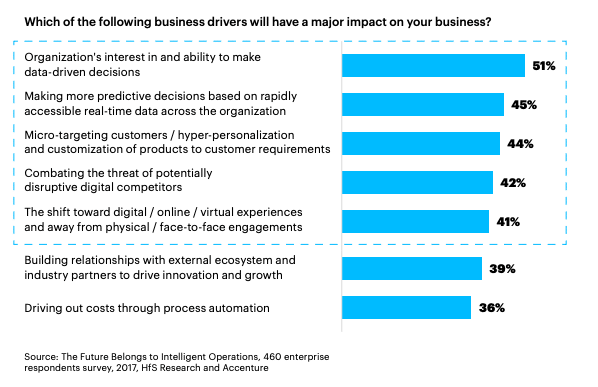
Flexibility allows data teams to adapt quickly as new insights or needs arise. Agile systems and protocols create a foundation for scalability and responsiveness. Accenture research shows agile data strategies improve data-driven innovation outcomes by 25%.
Human-Led Exploration
Automation and data-driven processes should complement, not replace, human insights. Allowing room for expert intuition drives innovative data use.
08
Chapter 08
Leveraging Data Automation for Efficiency and Insight
Data automation is a game-changer for organizations seeking to turn vast amounts of raw data into actionable insights. By automating repetitive, time-consuming tasks, organizations can streamline operations, enhance data accuracy, and empower teams to focus on high-level strategic analysis.
Data Processing and ETL (Extract, Transform, Load)
Automated ETL processes streamline the extraction, transformation, and loading of data from multiple sources into a unified data warehouse or lake. Tools like Apache NiFi, Talend, and AWS Glue facilitate real-time or batch data integration, reducing the time and effort needed for data preparation.
Real-Time Monitoring and Anomaly Detection
Real-time monitoring of key metrics, supported by automated alerting systems, enables organizations to detect anomalies, track performance, and respond quickly to emerging issues.
Predictive Analytics for Proactive Decision-Making
Predictive analytics uses machine learning algorithms to forecast future trends, customer behaviors, and operational outcomes based on historical data. These models help teams anticipate customer needs, optimize inventory, and enhance resource allocation.
Automated Reporting and Visualization
Automating data reporting and visualization saves time and ensures that stakeholders have access to up-to-date information. Platforms like Tableau, Power BI, and Looker provide customizable dashboards and automated report generation, delivering insights to decision-makers without manual effort.
09
Chapter 09
Establishing a Single Source of Truth for Reliable Data
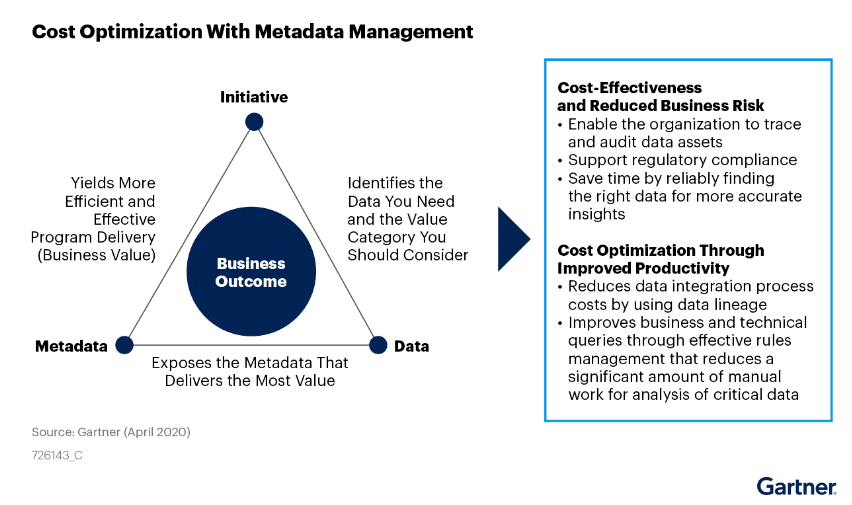
A data strategy should include a single source of truth (SSOT) that contains one authoritative copy of all critical data, serving as the cornerstone of reliable business intelligence.
A centralized SSOT (Single Source of Truth) fosters data consistency across the organization, reducing confusion and enabling reliable reporting.
Benefits of an SSOT
An SSOT ensures a single, authoritative version of data across departments, eliminating discrepancies and redundant data processes.
Implementation Best Practices
Establish governance standards and version control for SSOT maintenance, ensuring it remains a trusted data source.
Create a Report
Prepare a report for stakeholders that summarizes what was achieved, what challenges were faced, and any recommendations for the future.
10
Chapter 10
The ROI of a Well-Executed Data Strategy
A well-executed data strategy isn’t merely an operational choice but a strategic advantage. By aligning data goals with core business objectives, committing to continuous improvement, and leveraging modern tools, executives can build a foundation for data-driven growth that ensures measurable ROI.
An aligned, flexible, and well-executed data strategy delivers financial returns, enhances operational efficiency, and supports a long-term, data-centric culture—positioning the organization for sustainable growth and innovation.
Schedule 30-Minute Consultation With Orases Today
"*" indicates required fields

















