The Business Owner’s Handbook For
SaaS Applications
This guide to SaaS business applications will provide insight for business owners into the development & deployment of an application using the SaaS model.
Don’t feel like reading? Listen to our guide as a podcast, powered by NotebookLM technology.
In order to attract new clients, retain current clients and maximize profits, organizations must be able to keep costs down and have their operations run efficiently. Software can account for a large portion of many companies’ IT budgets, but new innovations in Software-as-a-Service are transforming the way businesses of all sizes operate by providing seamless access to data more conveniently and affordably than ever before.
01
Chapter 01
An Introduction To SaaS Applications & The SaaS Business Model
Custom SaaS applications are ideal for businesses looking to diversify their revenue streams through a subscription-based model.
Organizations that are seeking greater versatility, functionality and accessibility to gain an edge in a competitive business environment are turning to Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) applications and the SaaS business model. It is estimated that 86 percent of businesses will run entirely on SaaS by the year 2023[1].
SaaS is a method of software licensing and delivery that entails users accessing software online through a subscription, instead of purchasing and installing it on each individual computer. The software is hosted on servers managed and maintained by the SaaS provider. For example, Microsoft Outlook is an email application that follows the traditional desktop model, while Gmail is an email application that uses the SaaS model.
SaaS is used in a broad range of software, including e-commerce, business development, marketing, sales and productivity.
There are multiple advantages to using this approach for both users and developers, which has caused this sector to rise dramatically in a relatively short time. In fact, Global IT research and service management company Gartner predicts[2] the service-based cloud application industry is going to be worth $143.7 billion by the year 2022 as more organizations take advantage of the many opportunities awaiting in this sphere.
Some of the main benefits of using SaaS solutions include instant access from anywhere a user is working, greater flexibility and scalability, significantly lower upfront costs, automatic feature and security updates, and a reduced carbon footprint. Organizations can also eliminate the need for heavy infrastructure investments, maintenance and upgrades when choosing SaaS over traditional software.
Understanding how SaaS works and how it can benefit an organization is essential for choosing the right solution. This guide explores popular types of SaaS applications and how the SaaS business model works, along with the benefits of having a custom SaaS application developed. It will also cover important considerations for organizations considering this route, such as pricing models and strategies, technical considerations, financial considerations and the development process.
Popular Types of SaaS Applications
Cloud-based software can be created for nearly any task imaginable, from education and accounting to social media marketing and hotel management. Outlined below are some of the most popular types of SaaS applications.
Customer Relation Management Solutions (CRM Software)
Customer Relation Management (CRM) solutions automate the often-complex processes businesses use for sales and marketing, and growing businesses in particular can benefit significantly from CRM SaaS solutions.
The effective management of customer profiles allows organizations to better stay on top of their relationships with customers and provide them with a more personalized experience, which can have a very positive impact on customer retention and inspire repeat business. In addition, such systems enable them to address complaints and queries from customers quickly and effectively, further enhancing customer satisfaction.

Orases developed a custom CRM software solution for Next Day Dumpsters, which covered the MVP functionality of their existing pricing & quoting system and order tracking system.
SaaS solutions for customer relation management automatically track the interactions involving each client across various channels, including website, email, customer reviews, social media and support logs. Some are also equipped with artificial intelligence tools that allow communications to be personalized based on the data collected and past experiences.
Knowing what customers think about their products or services can make a big difference in the success of small and medium-sized businesses, which depend heavily on their ability to acquire new customers and retain existing ones. This information allows them to tailor their offerings and address any concerns before they lose their clients to the competition.
The ultimate goal of CRM SaaS solutions is improving organizations’ profitability through the improved business relationships that arise from effective sales and contact management. This applies not only to current and prospective clients, but also suppliers and service users.
Ideal For:
Businesses of all sizes that want to improve sales
Organizations that have sales and marketing arms
Businesses that need more effective customer services workflows
Organizations seeking a greater understanding of the effectiveness of sales and marketing campaigns
Smaller businesses that are expecting or experiencing periods of significant growth
Organizations that need to manage valuable, long-term accounts
Enterprise Resource Planning Software (ERP Software)
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software allows organizations to manage all of their business processes in real time. It can handle tasks related to accounting, risk management, procurement, project management, compliance, budgeting and supply chain. Traditional ERP software can be complex, but SaaS ERP systems are designed to be easy to adopt.
ERP software can increase revenue and enhance customer satisfaction by providing a single, up-to-date source of accurate information while avoiding data duplication. SaaS ERP software offers better and faster scalability and significantly shorter deployment times than traditional ERP software.

Orases developed a custom ERP application which automated work order planning, scheduling and execution for managing contract maintenance for Roy Jorgensen.
SaaS ERP offerings use a common database to keep workflows interconnected. They can provide consistent infrastructure, enhanced collaboration, greater user adoption rates, deeper business insight and reduced risk while lowering management and operational costs.
Ideal For:
Larger organizations with complex business processes
Businesses that need easier access to a range of information
Companies whose current IT infrastructure is too complex
Project Management Solutions
Project management software aims to improve the efficiency of project management teams via tools that assist with collaboration and progress tracking. SaaS solutions enable businesses of all sizes to embark upon their project management quickly and with minimal investment.
Managing projects requires constant updates, and this can become confusing and disorganized quickly using traditional solutions. However, SaaS project management software allows all information to stay accessible and up to date in real time so team members can make the most informed decisions possible.
The cloud component of SaaS project management solutions allows for teams to remain connected and access the system from wherever they are. Its low-maintenance nature means that teams can focus more on actual project management than dealing with technical aspects of the software. It provides team members with reliable access and eliminates the need to track down and send final versions of documents.
Ideal For:
Startups and small businesses that don’t have the budget for on-premise project management software
Businesses that work with a team of freelancers
Companies that have several physical locations and need to collaborate across different offices
HR / HRM Solutions
Human Resources (HR) and Human Resources Management (HRM) solutions allow businesses across all industries to efficiently manage all of their human resources-related processes, such as payroll, attendance, performance and many other tasks.
The quick implementation and great scalability of SaaS HR systems means that they are suited to unique situations as well as routine tasks. For example, when a business hires a new employee, they can quickly add a learning management system to help them gain the skills needed to carry out their role effectively.
SaaS solutions for human resources allow employees and managers alike to spend less time on administrative tasks, freeing them to focus on strategic initiatives that can move their business forward.
HRM systems can be developed to include a broad range of components. For example, they can handle tasks related to recruiting such as tracking applicants and scheduling and pre-screening interviews as well as job board posting. They can also handle talent management, compliance, performance management and analysis, engagement management, people analytics, employee reviews and reporting.
Ideal For:
Large organizations that manage thousands of employees
Smaller businesses that do not have a human resources department
Companies looking to reduce their human resources costs
Content Management System
A SaaS Content Management System (CMS) gives client users a powerful tool for managing their content in real time. It allows for a high level of collaboration as clients can simultaneously publish, create, edit and approve content such as web copy, artwork, documents and spreadsheets. This can reduce the time that is spent communicating back and forth between different departments about the status of documents and other types of content.
Advanced SaaS CMS security features such as detailed user activity logging, custom-defined roles and secure authentication allow sensitive content to be accessed safely. In addition, a SaaS CMS allows the quality control and oversight of websites to be centralized and unified, even as content creation and customization is handled by in-market teams. Top-down monitoring and the enforcement of compliance rules and brand standards can allow enterprises a higher level of compliance and quality control.
Ideal For:
Digital marketers and media companies
Websites of all sizes
Businesses that want to expand their online presence
E-Commerce Applications
E-Commerce applications for commercial transactions that take place online can cater to a broad range of industries, from digital offerings like eBooks and gaming to contracting services and physical goods like clothing and toys. They offer functionalities such as shopping carts, product information management, and marketing capabilities, among others.

Orases developed an e-commerce web application for Fencing Direct that could market their product to a virtually untapped audience nationwide to showcase over 10,000 products.
SaaS e-commerce applications are out-of-the-box solutions that allow organizations to launch online stores in a quick and affordable way that works seamlessly with their website and other solutions they are using. These applications can offer multiple platform options to accommodate diverse business needs. Many SaaS E-commerce applications offer technical help and customer support facilities as well.
Ideal For:
Small and medium sized businesses that sell goods or services
Newer businesses and entrepreneurs who are setting up shops online
Large companies that need help handling high order volumes efficiently
Learning Management Systems
A SaaS Learning Management System (LMS) is a platform for learning that provides users with the benefits of cloud computing. It is typically aimed at deploying and tracking online training initiatives. Anyone who has a login and password can access the provided online training resources any time they wish and from wherever they happen to be.
This means companies do not need to buy eLearning software products and install them on their servers, allowing them to devote more resources to other tasks. Moreover, they offer organizations the power to track learner engagement, assessment results and other metrics to identify trends and find areas for improvement.
Another benefit of SaaS Learning Management Systems is that they enable organizations to assign specific learning paths and training resources to individual learners so that each user receives personalized training that aligns with their job duties and learning goals.
Modern SaaS Learning Management Systems are incredibly user-friendly, giving end users a great degree of flexibility and control over their eLearning programs. They are fine-tuned to ensure that end users’ needs can be met without problems or downtime, and custom options can be created that allow businesses to meet their corporate learning goals.
Ideal For:
Organizations of all sizes that need to train employees
Companies that offer courses to the public
Freelancers in the eLearning space who deliver courses to multiple clients
These are just a few of the most popular SaaS applications. Niche and specialty solutions can also be developed that address the specific needs of different types of businesses, from yoga studios to pet hotels.
Custom SaaS applications can give a broad range of organizations solutions that are optimized for their particular processes, providing them with far more capabilities than generic solutions can offer.
SaaS Business Model & Stages Of A SaaS Business
Organizations that employ the SaaS business model benefit from recurring revenue and predictable cash flow, along with the ability to roll out new features as they become ready.
Providing a powerful online tool for a recurring monthly fee is an attractive business model, but it can be more difficult for companies entering the software realm to understand SaaS than other models.
Outlined below is an introduction to the three main stages SaaS businesses undergo.
Startup Stage
After coming up with an idea, talking to potential customers, and seeking financing, the startup stage is when the wheels are set in motion for the SaaS business. It entails creating and programming a working product and marketing it to new customers and is sometimes also referred to as the product/market fit or validation stage.
This is when the business acquires its first few customers, aiming to get enough users to see whether people will be adopting the product in the long-term or abandoning it.
Some of the common activities seen during this phase include:
- Finding channel/market fit
- Establishing and implementing metrics and analytics
- Securing angel or seed money
- Refining the product and its core features
- Making hey hires
- Securing the first paying customers
Hypergrowth Stage
When the market likes a product, there is a good chance it will enjoy significant growth rather quickly as businesses start to adopt the software. At this point, there is a good product and market fit, and traffic, leads and conversions are all on the rise. It is a stage marked by a rapidly expanding demand for data, bandwidth and technicians to support the volume of new customers.
It is important to note that the inability to successfully manage the hypergrowth stage is a common point of failure for many SaaS companies who are not properly prepared. To be successful, companies should avoid having a target customer that is too broad and make hiring decisions carefully.
Some companies may find it is best to shift their focus from growing revenue to profitability at this point. It may also be necessary to raise more capital to support more aggressive scaling and customer acquisition.
Some of the common activities seen during this stage include:
- Acquiring customers more aggressively
- Setting a firm and repeatable sales process
- Obtaining a deeper understanding of conversion optimization and A/B testing
- Seeking Series A funding
- Ensuring alignment between the product, marketing and sales teams
- Hiring executives
Stability Stage
The stability stage, also known as the maturity stage, is when the SaaS business model begins to level out. The company is earning a healthy profit from the SaaS and acquiring new users relatively quickly without restraining their infrastructure limits the way that the hypergrowth stage occasionally does. This is the point when businesses will also start to experience churn.
At this point, the SaaS company is a prime position where it has momentum behind it and stability ahead. This allows it to take advantage of its talent, market influence and revenue to try something new while enjoying the safety net of a reliable core business.
To remain successful, it is necessary to monitor the market and change with it, test out new products and tools, and maintain a competitive edge.
Some of the common activities seen during this stage include:
- Continued investment in growth and experimentation in search of further opportunities
- Putting local teams in place with a view to global expansion
- Considering adding new products or services
- Deciding whether to offer an IPO
- Identifying potential acquisition opportunities that align directly or tangentially with the current product
02
Chapter 02
Benefits Of Developing A Custom SaaS Application
Custom SaaS solutions give businesses the functionality they need to meet their unique goals without the concerns associated with complex hardware and software management.
As the need for custom software continues to grow, taking a business to the cloud via SaaS offers several important advantages. Although some businesses may operate within the same industry, their processes and software needs can vary dramatically.
Outlined below are the key advantages of developing custom SaaS applications.
Minimal Implementation Costs
Buying and installing traditional software can be a very expensive endeavor. Choosing Software as a Service enables businesses to eliminate these implementation costs while also saving on ongoing costs such as maintenance and upgrades.
In addition, because SaaS is downloadable and requires little to no maintenance, businesses can save significant money on hardware resources. Organizations only need to spend money on the specific software services they truly need rather than wasting funds on licensing for applications they will not end up using.
Seamless Integration With Existing Software & Systems
Custom SaaS applications can be seamlessly integrated with existing software and systems as well as third-party services such as marketing platforms, CRM, and live chat using existing or custom APIs. Most SaaS apps do not need to be installed and do not require devices with high-end specifications. A web browser and stable internet connection are generally the only requirements.
Using an open API allows users to integrate apps with their other legacy systems and commercial apps. Integration with other services gives clients the power to tailor solutions to their needs while enjoying the efficiency of a single connected system.
Improved Data Integrity & Removal Of Data Silos
Data integration is growing increasingly vital to the way business is done, and custom SaaS software can be designed in a way that maximizes data integrity and eliminates the data silos that can bog down operations. Data silos occur when information is only accessible by one department or is not easily accessed using other systems. Improperly integrated data causes these silos, and the result for organizations is reduced efficiency and inconsistent information.
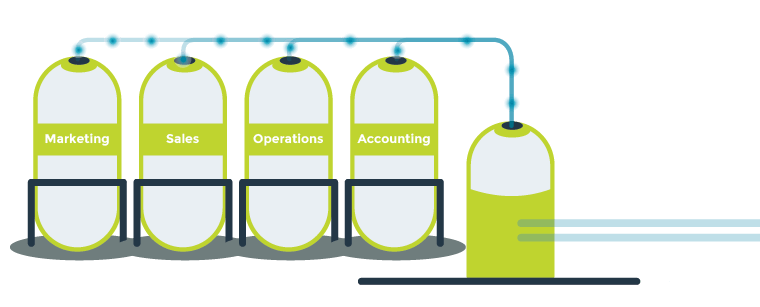
For example, a retailer might need their storefront app to query their inventory database to confirm stock, pass financial data on to a third-party processor for approving credit card payments and billing, and send the details of orders to their applications for warehousing and fulfillment. This is followed by apps for shipment scheduling and updating customers’ buying histories. Custom SaaS applications can take advantage of cloud technology to consolidate these apps, dismantle silos and ensure seamless data integrity and smoother operations.
Increased Ability To Scale With Future Needs & Requirements
When custom SaaS software solutions are developed, every step is carried out with future scalability in mind. Instead of acquiring new software licenses or increasing server space, it is simply a matter of getting another subscription or upgrading the existing plan for a relatively low cost. Businesses get the flexibility to scale software up and down as and when needed with SaaS.
Advanced Security Measures & Data Recovery Capabilities
Custom SaaS solutions give organizations a very safe platform where they can feel confident about storing their sensitive business data thanks to the latest developments in security. In fact, SaaS is a more secure option than traditional data storage methods because the applications, data, servers and platforms are managed and protected by data security specialists. This can be outsourced to a cloud provider with expertise in IT security for the ultimate peace of mind.
In addition, when a business has its IT data and infrastructure stored and installed in the cloud, it is protected from all manner of disasters. A fire, earthquake, flood or storm could leave a business without access to needed applications when they are stored locally. However, with SaaS and the cloud, businesses can continue to work uninterrupted from another location. With research from Gartner estimating that IT downtime costs $5,600 per minute on average[3]https://blogs.gartner.com/andrew-lerner/2014/07/16/the-cost-of-downtime/, the value of this advantage is clear.
03
Chapter 03
Benefits Of The SaaS Business Model
When compared to other as-a-Service business models, SaaS is often the most highest-value model as it provides several benefits for both business owners and their buyers.
The SaaS business model is popular among vendors for several compelling reasons. From the prospect of a recurring stream of revenue and more predictable cash flow to the ease of updating and improving offerings, here is a look at what makes SaaS such an attractive option.
Recurring Stream Of Revenue
One of the biggest benefits associated with the SaaS model is having a recurring stream of revenue. Although those that are switching from a one-time upfront payment model to a subscription-based model might experience a slower stream of revenue initially, the revenue that the subscription model generates over time will typically overtake that of the upfront model.
Smooth Sales Life Cycle
The sales life cycle of SaaS is often far smoother than other business models. Most of these solutions are priced at a per-user rate or on a monthly basis. This makes it easy for users to calculate their software costs and make buying decisions, eliminating friction that can arise when vendors must contend with IT budget approvals.
Increases Adoption Rates
SaaS is a smart business model because customers are far more interested in tools that can be used anywhere in the world than an offering that is limited to the specific device on which it has been installed, as is the case with traditional software. Users who are able to experience immediate benefits when using software are far more likely to commit to the product.
Easier To Provide Support
Another big benefit of SaaS is the potential to offer users support during free trials. Instead of calling or waiting for someone to come in person to solve installed software issues, support can be given to users immediately 24 hours a day, 7 days a week online. In addition to improving the customer experience, this gives them the maximum amount of time to become familiar with the software and its features and increases the likelihood they will go on to adopt the software and upgrade to a paid level when their trial is over.
In addition to support at the crucial free trial stage, ongoing support is easier with the SaaS model because the owner of the SaaS company has full control over the system and the environment in which it is being developed.
Ability To Improve & Update Products Consistently
Updates to SaaS software can generally be carried out without causing any expensive downtime for the company. In cases where an upgrade does require some downtime, the maintenance window is typically significantly shorter with SaaS software upgrades.
04
Chapter 04
What To Consider When Moving To A SaaS Business Model
The SaaS business model carries its own benefits and disadvantages that business owners must be aware of before making the switch.
Moving to a SaaS business model can be a wise business decision, but there are some important choices that need to be made along the way that can have a big influence on the success of the endeavor.
Choosing the right pricing model will directly affect your bottom line, but it is also important to use a good pricing strategy while keeping some important technical and financial considerations in mind. In addition, there are some crucial considerations when forming and managing the SaaS team. Outlined below are some important factors to keep in mind when making this transition.
Choosing A SaaS Pricing Model
Pricing is one of the biggest decisions an organization will make when embarking on a SaaS project. Many startups fail to give this aspect the attention it deserves, and it can be challenging to change to a more favorable pricing model after the software has been widely adopted. The pricing model needs to be weighed carefully to find the right balance between providing value and bringing in enough revenue.
The goal is to help customers and receive fair compensation for that help. Overcharging will drive away potential customers and make growth difficult, if not impossible. However, undercharging could leave the organization unable to recoup the costs of development and delivery.
Here is a look at the most popular SaaS pricing models and the major advantages and drawbacks of each approach.
Flat Rate Pricing Model
When it comes to simplicity, flat rate pricing is hard to top. It is a very straightforward solution that is similar to the software licensing models used in the pre-cloud days.
With this approach, a single product is offered with a single set of features at a single price in a one-size-fits-all solution. For example, a company might choose to offer access to every feature of its product for a single monthly price of $200. All parties involved know what to expect; the provider is getting $200 for every customer, and the customer gets unlimited use of the full product.
Usage-Based Pricing Model
A usage-based pricing model can be thought of as a “pay as you go” approach. Those who use more of the service will see their bill rise, while those who use less of it will spend less money as a result. The cost, in other words, is linked directly to usage.

There are several ways this pricing strategy can be used in practice. Software companies handling infrastructure and platforms like Amazon Web Services charge companies based on factors such as the number of transactions that are processed, the gigabytes of data they use, or their number of API requests. An accounting tool using this model might charge customers per invoice. Others are adapting the model in different ways, such as social media tools that charge users per scheduled post.
Tiered Pricing Model
With a tiered pricing model, companies offer customers a set of packages that contain different combinations of features at various price points. The tiered pricing model is favored by many companies in the SaaS sphere because it enables them to target a broader range of customers with different needs and budgets. For example, three packages with low, middle and high price points might be offered.

Some companies tailor each tier to a certain type of potential customer, with a basic package at a low price geared toward those who are new to the industry ranging up to an enterprise-level offering aimed at power users.
Per-User Pricing Model
With a per-user pricing model, a single user will be charged a fixed monthly price. If another user is added, the price will double, while a third user will cause the monthly costs to triple. This plan makes it very easy for clients to understand what they are getting with their monthly subscription, while SaaS startups will be able to predict and manage revenue more accurately.
This is the most popular pricing model used by SaaS companies, and many of them offer customers the option to pay monthly or annually; often, a discount is offered as an incentive to pay for an entire year in advance. In addition, teams with more employees might be offered a lower price per team member.
Per Active User Pricing Model
The per active user pricing model is very similar to the per-user pricing model, but it allows for situations where some employees will end up using the software more often than others. It entails charging subscribers based on how active they are.
A team can enroll as many users as it would like when signing up for the product, but they will only be charged at the end of the month or billing period according to how many users actually used the product. This helps businesses avoid spending money on vacant places.
Per-Feature Pricing Model
Although many of the main pricing models consider users to be the common variable, features can be used as the value metric instead. With the per-feature model, a few pricing tiers are set up based on the functionality that each one offers. The more features that are included, the more a customer will pay. Packages that offer basic features will have a lower price, while those with all the bells and whistles will come with a higher price tag.

For example, accounting software might use a basic plan that offers features like tracking income and expenses. The next tier might also offer the ability to manage bills and add multiple users. The highest tier may allow for running reports and tracking time and inventory in addition to everything that is offered by the lower tiers.
Freemium Model
The freemium model stands out from the other approaches because it entails offering a product that can be used for free, along with additional paid packages that provide further functionality. It can be thought of as a modified tiered pricing strategy with the entry-level tier being an unpaid one that can encourage users to give the product a try.

The free tier is quite limited to encourage users to upgrade. This tier might be capacity-based, with those who exceed their allowance needing to upgrade to a paid package, or it might have use-case limitations, such as only being able to use the free package internally and a paid tier being needed to manage customers. Some will use a feature-based approach, allowing basic features to be used by free customers while leaving some desirable features in their paid packages.
Selecting A SaaS Pricing Strategy
The pricing strategy used by a SaaS business should be selected with an overall objective in mind, whether it is drawing in more high-value customers or a quicker expansion into new markets. Here is a look at some of the most popular SaaS pricing strategies.
Penetration Pricing Strategy
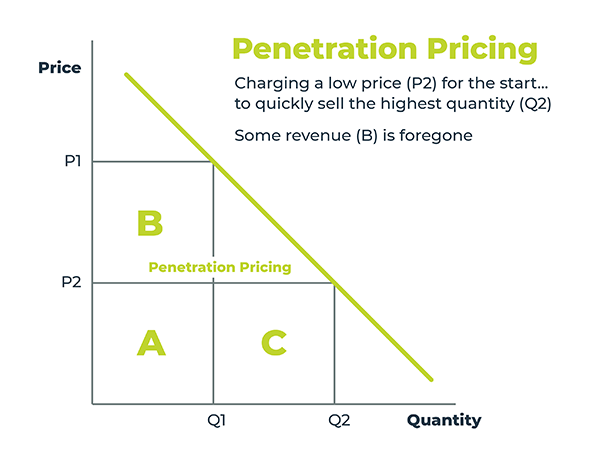
The penetration pricing strategy involves reducing prices in order to attract a slew of customers quickly within a target market. Some companies may reduce their prices to levels that are unsustainably low during the short term with the objective of compensating for those losses in the longer term, when they can upsell and cross-sell the large customer base they have amassed into more profitable packages. This may allow companies to claim significant market share ahead of their competitors.
Captive Pricing Strategy
Captive pricing is another common approach that involves offering a core product at a surprisingly low price while charging extra for additional products that are needed in order to get the most out of the product.
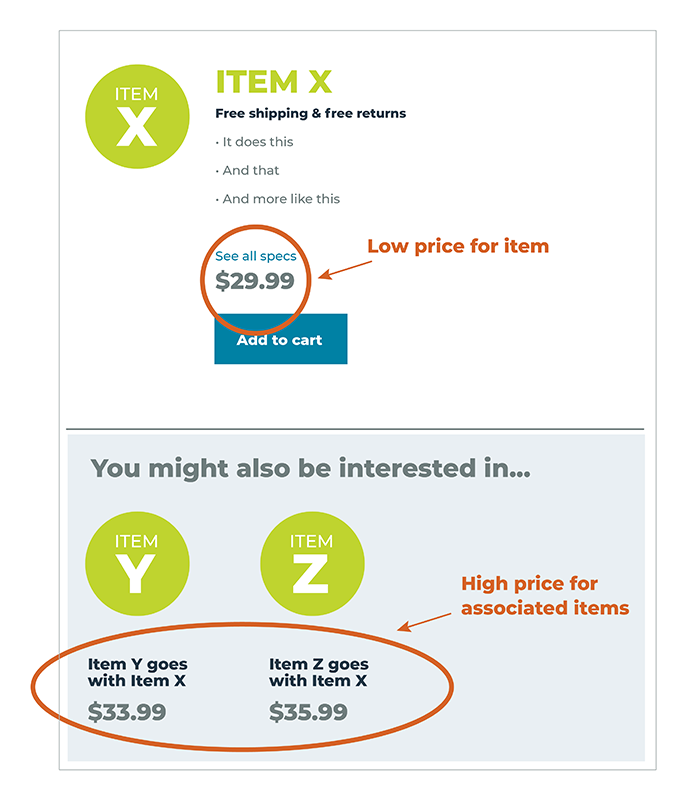
This can be likened to the approach used by consumer printers. Many home printers are sold at very low prices, but those who buy them must pay for expensive ink cartridges from the manufacturer that often amount to far more money than the printer itself. In this case, the ink cartridges are the captive product that the consumer is locked into paying for. Another example is Amazon’s Kindle e-reader, which is sold at a very low price, but owners must buy their books from Amazon in order to use it.
When it comes to SaaS software, one example is offering software for graphic designers at a very low price while requiring users to buy stock imagery from the same company’s stock photo service to use it.
Skimming Pricing Strategy
The skimming pricing strategy involves placing a high initial price on a new product that is eventually lowered over time. Also known as promotional pricing or writing down the demand curve, it allows the product to appeal to different subsections of the market as the price changes. It works well in SaaS because early adopters enjoy being the first to access new technology and are often willing to pay more money to be among the first. Later, as the product matures and its price drops, it will appeal to other parts of the market.
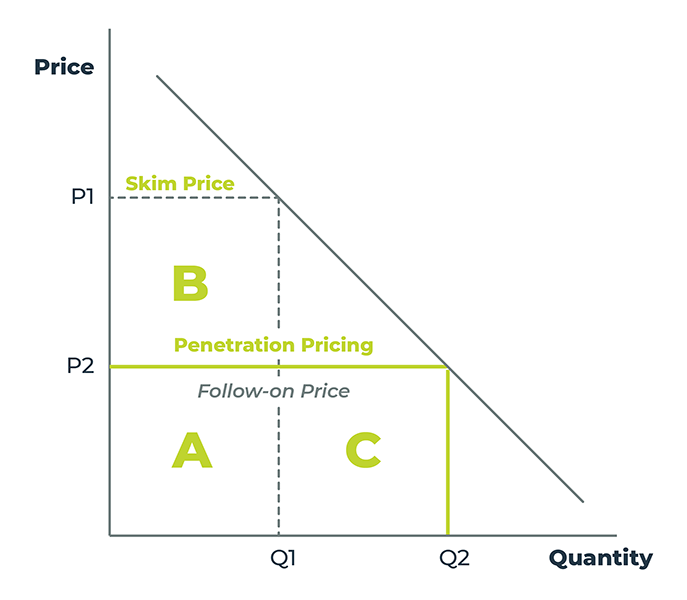
One of the most famous companies that uses this strategy is Apple. New iPhones and Mac computers carry a very high price tag that Apple enthusiasts are willing to pay as they enjoy the bragging rights of being early adopters. About a year after their products launch, just ahead of the launch of the next generation, these prices are reduced significantly, which attracts the subset of customers who are looking for a good value.
Prestige Pricing Strategy
Prestige pricing, or premium pricing, involves placing and maintaining a high price on a product to give it an aura of exclusivity or luxury. Although this may only attract a small customer base, those customers do tend to be higher in value.
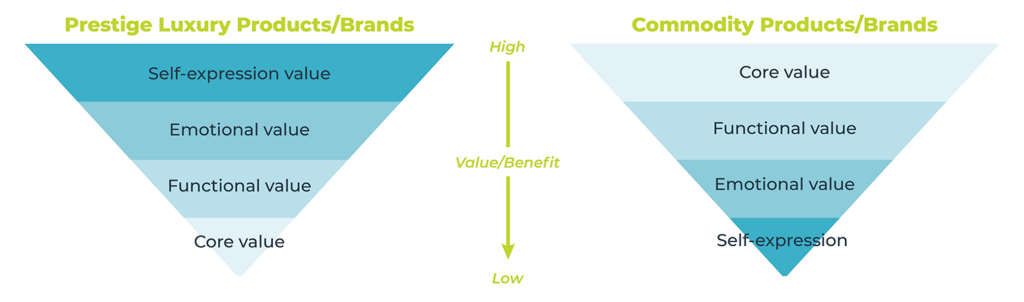
SaaS software providers whose products will be used by high-profile companies might be able to use this strategy to set themselves apart and differentiate themselves based on reputation. Some providers might use prestige pricing via a premium tier that gives elite customers top-of-the-line features and the recognition they desire.
Free Trial Pricing Strategy
Many SaaS providers opt for free trial pricing because it allows them to attract customers and get their attention without requiring any financial expense on their part. If the customer benefits from using the software during their trial, they have a strong incentive to upgrade when their trial has ended.

Some trials will be limited by time, such as 15 or 30 days, while others will be restricted based on usage, such as 10 social media posts or 5 file conversions. Companies that have a well-designed follow-up sequence are more likely to gain long-term customers using the free trial pricing strategy.
Cost-Plus Pricing Strategy
With the cost-plus pricing strategy, also known as cost-based pricing, SaaS companies add a target profit margin onto the costs that they incur for developing, marketing and selling their product. For example, they may decide that they will sell their product at cost plus 20%.
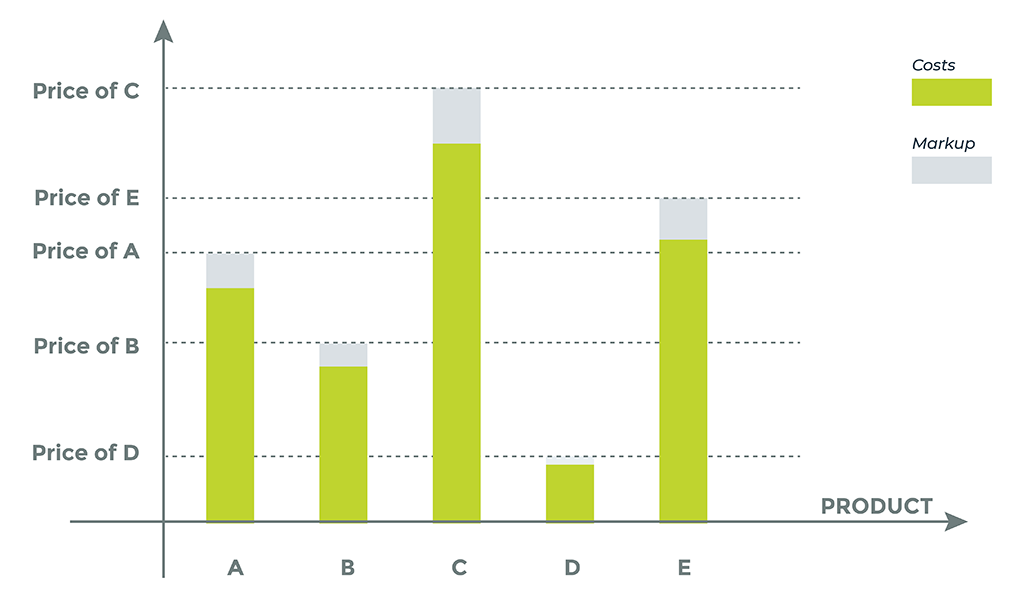
This approach does not consider the perceived value of the product, the customer’s price sensitivity or even the prices used by competitors. However, it can serve as a useful guideline in the early days of determining prices.
Value-Based Pricing Strategy
A value-based pricing strategy relies on the perceived value of the product as the basis for setting the price rather than costs, target margins or competitor prices. SaaS companies look at their pricing strategy from the viewpoint of the value it provides, and this is typically based on research that provides insight into how customers value such products.
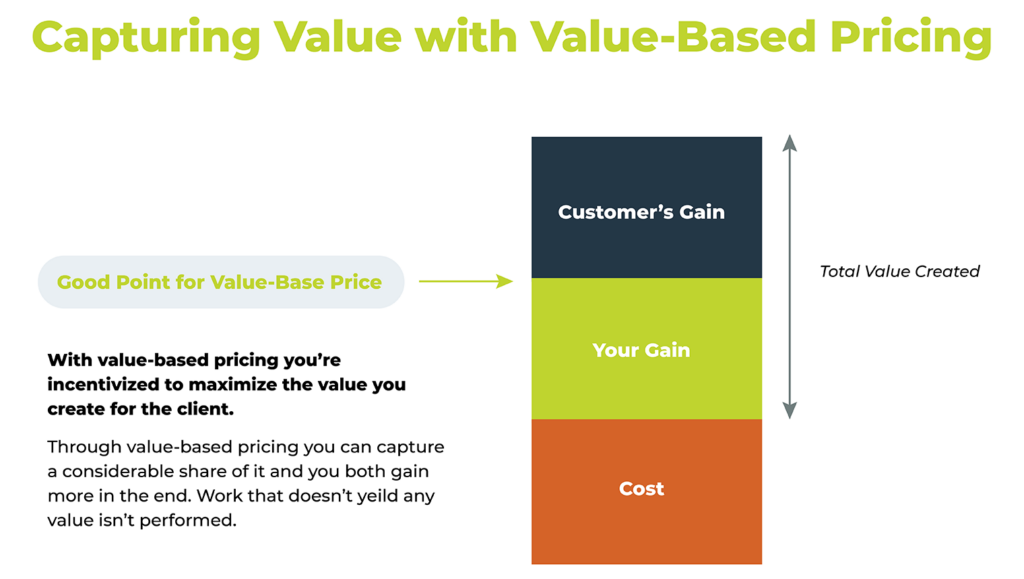
Many providers use the 10X rule as a guideline. This concept states that the value provided by the product should be 10 times its price.
Important Technical Considerations
After making the decision to switch from on-premise to SaaS architecture, it is important to consider several technical aspects to ensure a smooth transition with minimal risk.
Tool & Framework Migration Requirements
SaaS migration should be viewed as an incremental process. The early parts of planning will ideally focus on splitting the existing solution into parts that will be migrated to the new model and introducing the right tools and frameworks to carry out the migration.
Architecture Restructuring
During the planning stage, the current product’s architecture must be broken down and restructured. An app that uses a load balancer, web tier, application tier, and storage, for example, will see the web tier delivering the application assets, the application tier accessing the apps database, and the load balancer distributing the traffic to web servers.
Choosing A Migration Model
There are several potential migration models for SaaS, and the right one will depend on a provider’s specific business case. Here is a look at three of the most common options.
05
Chapter 05
Common Industries Which Benefit From The SaaS Business Model
While the SaaS business model certainly provides advantages for organizations across all industries, there are some industries that benefit from the SaaS model more than others.
SaaS is such a useful model that a broad range of industries can benefit from this approach. Here is a look at some of the biggest industries that benefit from using SaaS.
Manufacturing
SaaS has proven to be a valuable alternative to on-premise systems in the manufacturing industry in recent years thanks to significant developments in cloud technology. Many manufacturers are drawn to SaaS because of the lack of initial infrastructure costs and maintenance costs as the software company is responsible for maintaining servers. This also saves many manufacturers on the costs associated with training IT personnel.
The greater speed and flexibility offered by SaaS makes it incredibly attractive to manufacturers. Because getting started is simply a matter of signing up online, there is a very short time to implementation and the software can be accessed from anywhere, whether it is at the desktop or on shop floor operations.
Media & Entertainment
SaaS is increasingly favored by media and entertainment companies because it is uniquely suited to meet the demands found in these industries. The worldwide availability, effortless maintenance and automatic updates mean that freelancers can work in harmony with employees in multiple offices around the world without having to worry about maintenance and upgrades.
Many media companies need the ability to move their data quickly and seamlessly, such as in live coverage of breaking news or special effects for feature films. SaaS provides this with a high level of security and is able to adapt quickly to meet changing demands. It also is highly scalable and capable of working with large professional media files.
Logistics
Logistics management professionals favor SaaS solutions because there is no need to install, run, update and maintain software on every computer and device used by each worker. This can be a substantial headache for logistics managers in charge of large teams.
Many are drawn to the idea of nearly 100% uptime so they can focus on managing their warehouses or supply chains. SaaS also provides an excellent return on investment while allowing logistics companies to avoid security threats. Transportation Management System (TMS) SaaS solutions are particularly popular on account of their easy scalability and the ability to add or upgrade services on demand to keep up with the constantly evolving world of logistics.
Retail
Many retailers are shifting to SaaS because of benefits like a smaller learning curve, which means the offerings can be adopted quickly across the workforce. Confidentiality is another important consideration for retailers who handle sensitive customer data, and the security provided by SaaS gives them peace of mind while avoiding the need to hire expensive computer security experts to safeguard data. SaaS also provides the perfect solution to coordinating across retail outlets and corporate departments.
It is also beneficial to online retailers, who traditionally have had to make expensive investments into hardware, software and skilled labor to set up the infrastructure needed for an online retail store. Now, SaaS gives them the option to pay a reasonable subscription fee each month to a service provider to access the software needed to successfully run their e-commerce site. The lower upfront costs and easy implementation mean they can start doing business quickly and without interruptions.
Finance & Accounting
Fintech companies and banks can save significant operating capital every year by using SaaS offerings. Their high scalability allows financial companies to transform their processes digitally without having to worry about compliance and security. Some fintech lenders are using it to accept and process their business loan applications in record time, issuing eligible borrowers with their funds in a matter of just days.
Moreover, accounting and bookkeeping tasks performed in the cloud mean every piece of data is updated in real time, giving CFOs an accurate view of financial operations at all times to facilitate insight-driven decisions that can improve working capital. This is particularly important for business decisions that require a prompt response.
Many finance companies appreciate how SaaS services automate tasks like data analysis. They also find it useful for carrying out secure client communications.
SaaS finance and accounting solutions are more affordable than their on-premise counterparts, which is a clear selling point in the budget-focused finance and accounting sector. SaaS saves these companies on the costs and resources that would be needed to host their own servers and infrastructure in-house. In addition, its constantly updated nature and high security allows companies to avoid the security risks associated with using outdated versions of accounting software and staying on top of manual updates.
Notable SaaS Companies
Here is a look at some of the most notable SaaS companies that are inspiring startups today.
Salesforce
Salesforce is considered a pioneer in the SaaS space. They offer a complete suite of software for marketing automation, application development and customer service.
Salesforce got their start with a marketing campaign called “The End of Software” to draw attention to the idea of bringing software to the cloud. The company was founded on the premise that software should be available to people anywhere and anytime, and their user-first focus has earned them plenty of accolades.
Salesforce is widely considered one of the biggest SaaS companies thanks to a market capitalization of $207.35 billion. They currently offer 58 cloud computing products that allow employees to better collaborate with customers.

HubSpot

HubSpot markets and develops software products for sales, customer service and inbound marketing. Its most popular product is a free CRM offering that includes features such as tracking prospects and emails, live chat, and scheduling meetings. Its four major software suites employ a tiered pricing model.
It enjoys an impressive global traffic ranking in the online marketing sphere and is considered a major player within the SMB SaaS market. Founded in 2006, it grew in just eight years from nothing to more than $100 million in revenue, making it a true SaaS success story.
Mailchimp

The marketing software company MailChimp is a SaaS provider that offers three major products. It was launched by a pair of co-founders who were seeking a way to help the customers of their web design business send emails to clients and prospects.
Its star product, MailChimp, is a platform for email marketing that allows organizations to schedule the sending of automated emails and track the results of these campaigns. It uses a freemium model where some features are available at no cost, while upgrades unlock access to additional features.
Their quirky branding, customer service focus and freemium model are all identified as crucial elements of their success.
Microsoft

With more than 100 different cloud products across a range of software types, there is no denying Microsoft’s place as one of the biggest names in SaaS thanks to products like Azure SaaS.
The company also successfully brought its popular Microsoft Office suite of software to the cloud as a SaaS solution. For example, their popular word processing software Microsoft Word had to be purchased at a store and installed on computers in the past. These days, users also have the option of using it as a SaaS product, paying a monthly or yearly subscription fee to use it and receiving new features and updates on a regular basis at no additional cost.
Slack

Slack is best known for its eponymous collaboration and chat tool that facilitates communication for companies that work with remote teams. It offers features such as productivity bots, video conferencing and internal messaging to give everyone on a team a shared view of a project’s purpose and progress.
Its creators first tried to make a web-based massively multiplayer online game before realizing that their true passion was creating a communication tool like IRC. Many of Slack’s features, such as channels organized by topic, direct messaging and private groups, were inspired by IRC.
Slack’s success has been attributed to their focus on doing just a few things but doing them exceptionally well and a freemium model that has led to significant bottom-up, word-of-mouth growth.
06
Chapter 06
What To Know About The SaaS Application Development Process
There are several considerations that must be accounted for during the development of a SaaS application, including user intent and capabilities.
The SaaS application development process takes a SaaS offering from the idea stage to a working product that improves the lives of its users. The goal is to produce software with maximum quality in a quick and cost-effective manner, and a set flow of stages is used to make the process smoother and more effective.
Features & Requirements Prioritization
The heart of most SaaS applications is the features list. There is typically a long list of features and requirements to work with when creating applications, and it is essential that the SaaS development team understands which features and requirements are priorities before they begin their work.
It can be useful to start with the single most important feature and try to have it delivered as soon as possible so it can be shared with some potential users to get feedback. If the main idea is not well-received, this can avoid spending a lot of time and money on developing something that is unlikely to be successful.
When it comes to the other features, a good question to ask is whether the app can fulfill its main purpose without each feature. The features that the app could not exist without should be given priority over other features.
Prioritizing features and requirements is a crucial task, and it is important to take the time to carry out this task carefully and thoughtfully. Begin with the MVP and the “must-haves” before moving on to the secondary features and “nice-to-haves”.
Writing User Stories
User stories are an excellent way of communicating the goals of the software project to the development team. Stakeholders and team members can use user stories to communicate their expectations and requirements, which makes it more likely the end result will meet their vision.
User stories are typically just one or two sentences long, and they aim to describe how the system being developed should respond to a specific type of user’s actions. It is typically written from the perspective of the person who will be performing the action. One conventional template that is often used is the following:
As a {type of user}, I want {some goal} so that {some reason}.
This template, which is used in Scrum software development, can be applied to a broad range of users.
For example,
“As a power user, I want to specify which folders should not be backed up so that my backup drive won’t be filled with unnecessary files.”
“As an administrator, I want to be able to add other administrators to some projects so that I can delegate tasks efficiently.”
“As an internet banking customer, I want to set up recurring transfers so that I don’t have to enter the account numbers of recipients every time I pay monthly bills.”

Properly communicating the needs and requirements of a custom SaaS application to a custom software development team can be a difficult process. User Stories are used as an effective tool to promote transparency, project requirements & confirmation of feature goals among team members and stakeholders. Learn how to create User Stories by downloading our e-book here!
Application Prototyping
Designers can use prototyping tools to create proof of concepts that give stakeholders and users a feel for what is being built before the development process gets fully underway.
Prototypes allow developers to test information architecture, visual hierarchy, interactive elements and layouts to ensure everything will function as expected so they can move toward a completed solution. They range in complexity and may come in the form of paper prototypes, wireframes or clickable prototypes.
A prototype might encompass the entire product, or it could focus solely on some of the potentially complicated elements. Developers will view prototypes with mobile and desktop settings in order to identify potential flow or usability issues across different devices.
One of the biggest benefits of prototyping is saving time and money by ensuring the most expensive part of the process, full-fledged development, will be focused on the right factors. When misunderstandings are identified and addressed early in the design process, it can avoid costly mistakes.
It is also useful as it gets all parties involved in the design process, which is important when customers are using software development services to create their offering. Engaging with all the participants – including developers, project managers, business analysts, everyday users and designers – gives the project greater focus. The opportunity for collaboration that is provided by prototyping can set the tone for a very positive and successful project overall.
UI/UX Design
Prototyping is followed by the design stage. There are two main components to the design stage of a custom SaaS project: UI design and UX design.
A well-crafted user interface (UI) is a crucial feature for custom SaaS applications. UI teams will assess the project to find the best way for users to interact with the app and determine which features the targeted user base will seek. A solid UI design can make software stand out from the competition and increase conversions and sales. In addition, a professional-looking user interface can build consumer confidence in the software.
The user experience (UX) is where an application is going to have its biggest competitive advantage, which is why this area deserves significant attention. Good UX design will ensure the user’s journey is smooth and intuitive, with key elements positioned in a way to allow for simple navigation. This can lead to a higher conversion rate and more website traffic while keeping bounce rates down, all of which impact the bottom line. The right UX approach will result in a streamlined experience that keeps users engaged while avoiding frustration.
Development Of The Custom SaaS Application
The next part of the process is full-fledged development, which is typically carried out by an experienced SaaS application development company. Also known as implementation, building, or coding, it is when all of the planning and prototyping that have been carried out finally come together. If the previous stages of the process were carried out in an effective manner, implementation should be very straightforward.
Rigorous Testing & QA Of The Application
Once the coding has been completed, the software is put through a series of rigorous tests that are aimed at removing bugs and ensuring a smooth experience for all types of users across different devices.
Testing may be carried out manually or automated with testing software; both methods may be used by some developers to ensure all the bases are covered. Most of the testing will be carried out in-house by the software developers, but external users might also be brought in to test the software in some cases. If any issues are identified during testing and quality assurance, the software might be sent back into the production phase until it is ready to be deployed.
After passing tests and quality assurance, the code is prepped for deployment before being released and going live. This is when the client finally sees the final result of the project and how users interact with their software.
Continuous Maintenance & Support
After deployment, custom SaaS software moves into the continuous maintenance and support stage. Developers will monitor factors such as server load, offer production support and develop new updates and features based on feedback received from users. They can also address issues with the software that arise once it has been fully launched. New updates and features may be added at any point, and security and patches might also be part of ongoing support.













